SCIENCE SOURCE NEWS: Brought to you by Science Source, your source for stock science and photography, medical illustration, and video.
Tuesday, January 26, 2021
History of Prosthetics: From Ancient Egypt to Today
Medical Microscope - Gift Ideas for the Medical Professional
Monday, January 25, 2021
Down Syndrome Awarness
Last month was Down Syndrome Awareness Month. According to The National Down Syndrome Society, the month is an opportunity to spread awareness about people with Down Syndrome by celebrating their abilities and accomplishments, rather than their disability.
Stock image and video gallery of down syndrome awareness
Over the years, The National Down Syndrome Society has devoted itself to the specific health and education needs of people with Down Syndrome. The NDSS raises money through direct donations and fundraisers such as the Buddywalk each election year. They also advocate for legal protections for people with down syndrome and fight to preserve government assistance programs.
Down Syndrome is one of the most common chromosomal diseases, affecting about 6,000 newborns each year. While there is no cure for Down Syndrome, organizations such as the NDSS continue to provide people with the condition with the help and opportunities they need to live happy and fulfilling lives. As their website mentions, people with Down Syndrome drive cars, go to college, get jobs, date, and get married every day! Find out how you can help them fulfill their dreams by visiting the NDSS website below.
DNA and Genetics Themed Gifts and Home Decor
At Science Source, we proudly celebrate people from different backgrounds and experiences. We are excited to celebrate Down Syndrome Awareness Month by offering a broad and inclusive selection of stock images and videos.
Friday, January 22, 2021
Neurigenetics
Neurogenetics is the study of the nervous system as it pertains to genetics. Using phenotypes, or observable characteristics and traits, neurogenetics attempts to reach conclusions about individuals of one or more species on the basis of hereditary.
Seymour Benzer, considered by many as the father of neurogenetics, made his first discovery in the field of neurogenetics when he pinpointed a link between the circadian rhythm and genes. He found that animals go through cycles of sleeping and waking naturally and not by anything learned or developed. This led him to further investigations in the traits and behaviors of individuals as they relate to genetics. Benzer went on to make groundbreaking discoveries in neurodegeneration when he discovered similarities between fruit fly and human genes. This helped him isolate neurological diseases in humans.
Advances in molecular biology and the species-wide genome project have made it possible to map an individual's entire genome. While this information is key to understanding neurobiology, a comprehensive picture of an individual’s traits and behaviors can only be achieved by taking into account additional factors.
The classic debate of nature vs. nurture clarifies that one’s genes are not the only determinant of a given biological outcome. Science reveals that traits and behaviors are due to a confluence of many genes, as well as regulatory factors like neurotransmitter levels and one’s environmental influences.
New developments in genetic engineering are being used to alter genetic material to potentially negate or suppress the effects of genetically linked diseases. Innovations in technologies, such as CRISPR, allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome.
It is possible that one day genetic editing could be used to cure neurogenic diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's. Research on this front, however, is still ongoing.
Tuesday, January 5, 2021
Taking a Closer Look at Microscopy for Medical and Scientific Use
Read any scientific or medical news story and you can see that microscopy has come a long way since your high school biology class microscope.
It isn't just higher magnification, but crisp details, a greater depth of field, viewing internal features, and colorful 3D-like visuals that fascinate us. There have been many advancements to light microscopes and a multitude of new kinds that can see so much more than we could have ever expected.
Let's take a closer look!
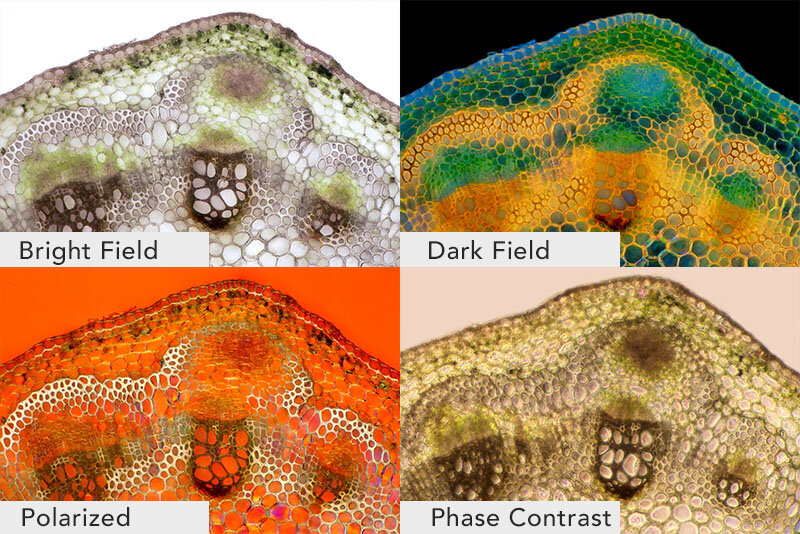
Four types of Light micrographs: Bright Field, Dark Field, Polarized, Phase Contrast. © Marek Mis/Science Source
The basic microscope we used as a kid is the standard “light microscope”. Simply put, it uses light and a set of lenses. The addition of filters, specialized mirrors, lasers, specific light spectrums, and other features gives us much more detail.
More advanced devices include Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM), Atomic Force Microscopes (AFM), and Scanning Tunneling Microscopes (STM).
Commonly used techniques when viewing slides on a light microscope are Bright Field, Dark Field, Fluorescence, Differential Interference Contrast (DIC), Phase Contrast, and Confocal microscopy.
Light MIcroscope Bright Field: the light source shines directly from underneath the specimen, creating a light-colored or bright area around it.
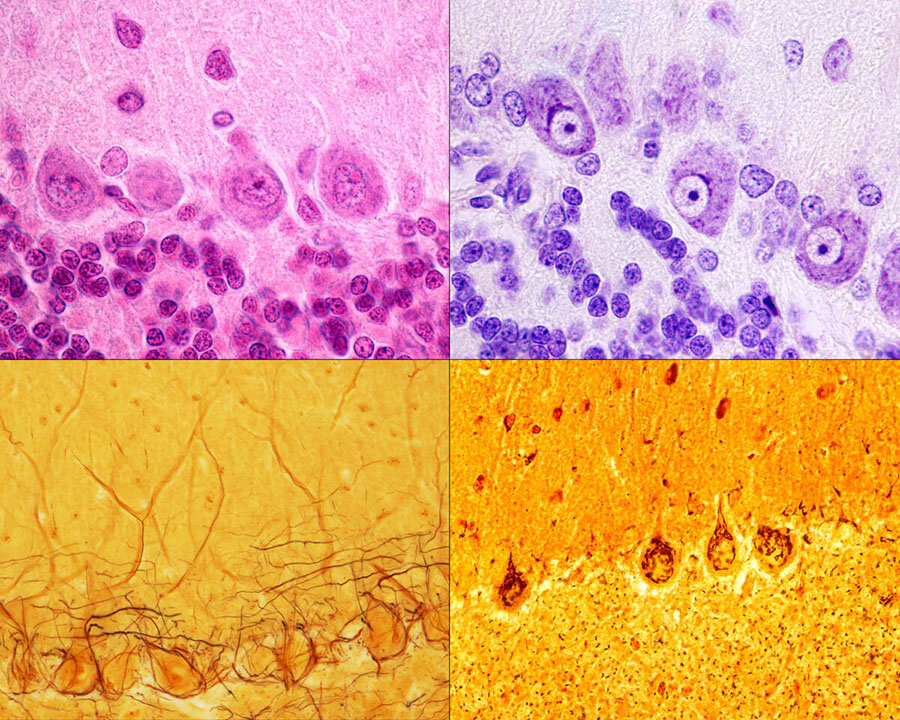
Purkinje neurons of the cerebellar cortex stained with four staining methods: hematoxylin eosin (top left), cresyl violet (top right), Cajal's silver nitrate (bottom left) and silver method for Golgi apparatus (bottom right). © Jose Luis Calvo/Science Source
Light Microscope Dark Field: the light source is occulted, so it reaches the specimen at different angles giving us slightly more varied details than if it was lit from directly underneath. The area around the specimen is dark or black.
Fluorescence: This uses light filters and specific wavelengths. Short wavelengths are reflected down to the specimen, which then fluoresces or gives off long wavelengths of light. These are reflected up to a mirror that allows long wavelengths to pass through to the lens.
Phase Contrast: Using a special lens and filters it allows viewing of transparent and colorless specimens. It looks similar to DIC micrography but lacks shadows, making it a bit more two dimensional.

Different illumination techniques of a light microscope: dark field, fluorescence, bright field, phase contrast, DIC (differential interference contrast). Child’s hair strand © Ted Kinsman/Science Source
Differential Interference Contrast Microscopy (DIC): Using a polarizer, beam splitter, condenser, and filters it allows viewing of transparent and colorless specimens. It has a more three-dimensional appearance than phase-contrast microscopy.
Confocal Microscopy: Also called Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM), it uses a laser and a spatial pinhole to create a sharper image.
Let's look at the more advanced types of microscopes:
Scanning Electron Microscope SEM: Uses a particle beam of electrons. It detects reflected electrons off the surface of a specimen, which is placed in a vacuum. creating sharp images. Magnification ranges from 20x to 30,000x, spatial resolution of 50 - 100nm.
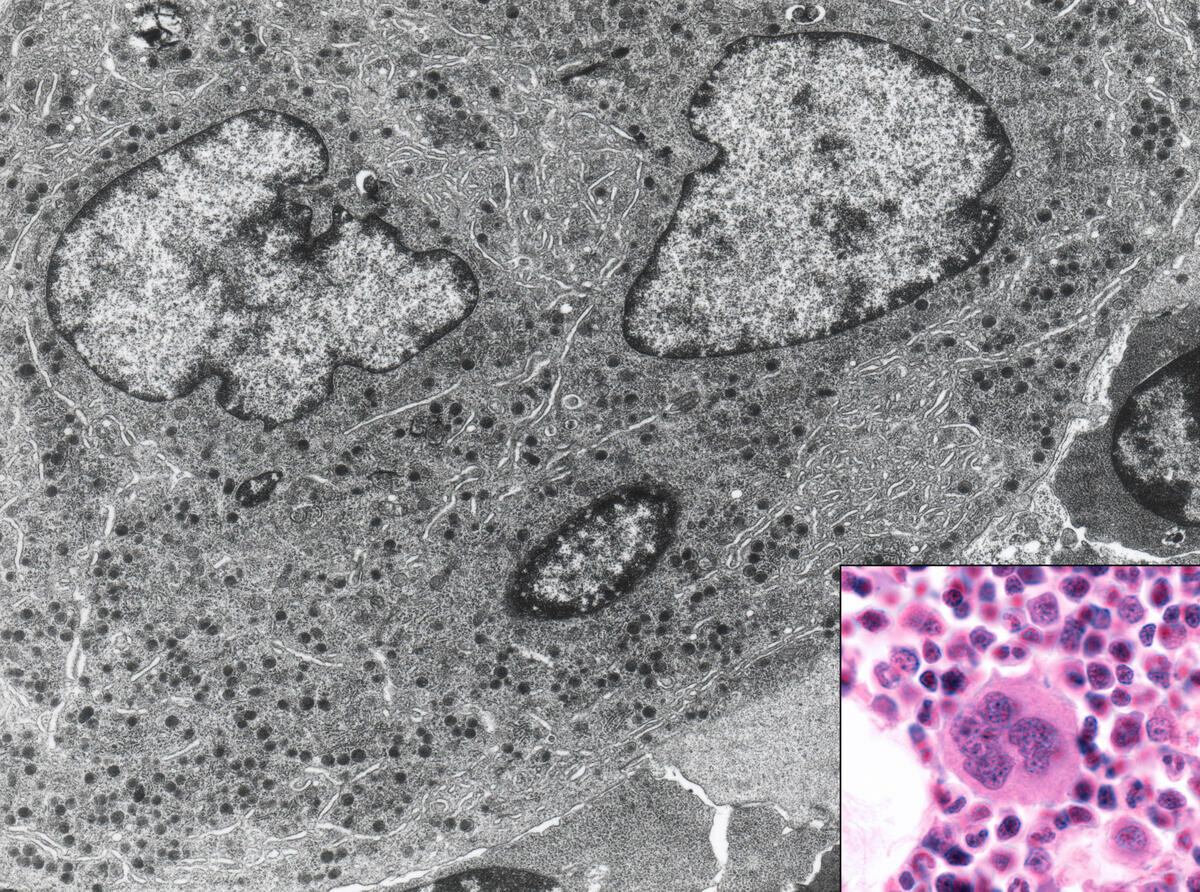
Bone marrow cell. This micrograph shows this cell with light (inset) and electron microscope. © Jose Luis Calvo/Science Source
Transmission Electron Microscope TEM: Uses a particle beam of electrons that pass through a thinly sliced specimen. It can show the internal structures of cells with a magnification up to 2,000,000x.
Atomic Force Microscope AFM: AFM uses a laser that bounces off of a stylus on a cantilever lever. This action traces the specimen. Any deviation triggers the sensors creating a raster image. One benefit of this is that it also records the Z-Plane. Another advantage of AFM over electron microscopy is that the specimen need not be in a vacuum.
Scanning Tunneling Microscope STM: Scanning Tunneling Microscope STM: An STM also uses electrons, based on quantum tunneling. The benefits are that it can be used in a vacuum, air, water, or ambient gas environment. It captures surfaces on the atomic level.
What can we look at with all of these scopes?
Scoop up pond water or ocean water to be astonished by the plethora of living zooplankton and phytoplankton visible within a single drop using a simple light microscope.
It opens you to the wonder of cyanobacteria, blue-green algae, ciliates like paramecium, daphnia, amoebas, and euglena. If you were lucky, you might have witnessed them conjugate and divide!
Additionally, the ocean water drop allows a peek at copepods, immature mollusks, krill, algae, crustaceans, fish in their zooplankton stage; and you may behold the breathtaking beauty of diatoms, the most common type of phytoplankton in our oceans.
Switch to a higher-powered Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) to view Water Bears, pollen, blood cells, and insects. An SEM uses a particle beam of electrons to photograph the surface of a vacuum-sealed specimen.
Transmission Electron Microscopes(TEM) allows us to see cross-sections of a specimen like the beautiful interior of the human body, marine life, and animal and plant cells. The TEM's particle beam passes through its vacuum sealed specimen.
Custom homedecor, phone cases, shirts and more.
Of course, there are critical medical applications.
We can view the cells of the human body with many different microscopes. The light mic, SEM, and TEM show scientists and medical researchers different angles and aspects of the cell and its fine structures and organelles.
Microscopes help scientists study cancer - breast, ovarian, prostate, liver, and skin cancer. We can develop an improved understanding of skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema. They assist in the fight against nervous, respiratory, and circulatory system diseases. And a cure for muscular conditions such as fibromyalgia and multiple sclerosis (MS) and autoimmune conditions.
Infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, prions, and parasites can be examined. It allows us to better understand, diagnose, and work towards cures, vaccines, or prevention.
And without the microscope, how could we progress in the fight against the seasonal flu, measles, polio, malaria, and HIV/AIDS.
If light, lasers, electrons, and quantum physics are not enough, there is even a microscopy method, similar to SONAR, that uses sound waves; Acoustic Microscopy.
Lastly, without these microscopes, we would not be able to continue our current fight against the Coronavirus, COVID-19.
Tuesday, December 22, 2020
Medical Micrographs: a View into the Human Body
science has advanced exponentially in the last century. Even just the way the human body and pathology are viewed. We’ve gone from the basic x-ray to be able to see a single cell in the human body. Or even smaller.
One of the most fascinating innovations has been the Scanning Electron Micrograph, often referred to simply as an SEM for short. It has revealed hidden worlds of the human body, medical, and of course the natural world as well.
Gallery of Medical and Anatomical SEMs (micrographs) Stock Photography
The scanning electron microscope was invented in 1937 by Manfred von Ardenne the SEM machine uses electrons to record the surface topography of objects.
Thursday, February 13, 2020
Bringing to Light, Creatures of Darkness

Friday, December 20, 2019
The History of Christmas
As people put up Christmas trees and decorate their homes, it’s easy to believe these traditions have been around since the year one, but Christmas and the holidays surrounding December 25th have taken many forms.
The origin of Christmas comes from three sources: it is the date of the winter solstice on the Roman calendar, it is about nine months from the vernal equinox (March 25th) and it is the date set for the birth of Christ.
Before Christendom the Roman Empire celebrated Saturnalia, a holiday honoring the Roman god, Saturn, the farther of Jupiter. During Saturnalia social customs were flipped upside down. Slaves ate at their master’s tables, women flirted with men and gambling was permitted. Saturnalia also involved public banquets and gift giving, which may have influenced later Christian traditions. There were even reports of naked caroling!
Origins of Christmas stock Image Gallery
The Christmas tree has its origins in 16th century Germany. While writing a sermon at night in a starry evergreen forest, the Protestant Christian reformer, Martin Luther, is said to have added lighted candles to a tree and put it into his house. Other Protestant Germans brought similar trees into their homes and the tradition spread. By the second half of the 19th century, the tradition had moved beyond Germany, first among the upper classes and eventually into lower areas of society.
While you are making your shopping rounds this holiday season, attending religious services or making time to be with family, reflect on the long history behind the season. Be sure to also check out great holiday gifts below and click the links above to see more historical images of the origins of Christmas.
From all of us from Science Source Merry Christmas and Happy Holidays!
Rotifers, Nematodes and Tardigrades Stock Microscopic Photography
Roti fers (Philodina sp.), Light Micrograph The bdelloid rotifer, found in freshwater habitats all over the world, is able to withstand ex...

-
s it a twig or an insect? A harmless moth or a scary owl? Animals have amazing tricks up their sleeves to protect themselves, take adva...
-
A Telescope Fish has eyes that can track bioluminescent prey. The world can feel like a small, crowded place, but actually, two-thi...
-
The idea of bacteria creeping through your body might be less than appetizing. We often associate the presence of bacteria in our bod...



















